PESA-MESA-TESA
Table of Contents
What is PESA-MESA-TESA?
PESA, MESA and TESA, which are preferred in cases where sperm are not found in the semen, such as azoospermia are the treatment techniques performed so that the patient can be fertilized with their own gametes. Different techniques for sperm assisted reproduction have been developed in cooperation with today’s modern and technologically equipped laboratories and a team of experts in IVF treatment. In this way, the sample quality in the treatment process has been increased, surgical methods have been diversified and the chance of giving birth to a healthy baby has increased. Techniques and surgical sperm retrieval methods applied for many cases such as vaso-atresia, vasectomy, and cystic fibrosis, have allowed successful results. In all three methods, the aim is to collect sperm from the man and to extract a high amount of sperm in order to start the pregnancy process.
Some of the indications that require sperm intake can be listed as follows;
Some of the basic techniques used to obtain sperm in IVF treatment are as follows;
PESA : Percutaneous Epididymal Sperm Aspiration
TESE : Testicular Sperm Extraction
MESA : Micro-Epididymal Sperm Aspiration
The main purpose of preferring the applications is that some individuals cannot reach the sperm plaster as a result of blockage in the sperm canal or the destruction of any part of the testis. In such cases where semen analysis called spermiogram is applied, the sperm cell is not visible. This condition, called azoospermia, makes it necessary to obtain sperm cells from the testis using a small surgical biopsy technique.
TESA or PESA?
The TESA method is the examination of a piece taken from the sperm testicle in a microscopic environment by microsurgical method in cases where there is no sperm in the epididymis or there is no epididymis. Various samples are taken from the tissues that are enlarged up to 20 times in the application performed by opening a sac in the testis. In these samples, sperm cells are absent or limited in number. In such cases, a surgical method called TESE is applied.
Micro TESA method is the application of obtaining sperm from the testis through biopsy. During the procedure, it is possible to see the vascular structures of the capsule surrounding the testicular tissue and to make an incision without damaging the relevant vessels. This also reduces the risk of complications. The application, which multiplies the probability of finding sperm, is performed under general anaesthesia. The patient can be sent home after the patient regains senses. Micro TESA application with local anaesthesia is not preferred much because the patient remains immobile for a long time and can be affected psychologically during the operation.
The PESA method, on the other hand, is to obtain sperm cells by reaching the epididymis area with a biopsy needle from the structure called scrotum skin that covers the testicles of the man. The sperms used in the ICSI method are withdrawn from the epididymis with the help of an injector. This method is used only in cases where the vas deferens are blocked (obstructive azoospermia).
It is possible for patients diagnosed with azoospermia to have children with TESA application by applying in vitro fertilization treatment. It is an application that increases the chance of having a child, especially for young patients and when there is sperm production. If sperm cells are found during the procedure, rapid freezing can be applied in embryology laboratories. In this way, the cells can be used in the next IVF treatment process. This means that even in case of failure, the treatment can be started again.

What is the procedure for PESA?
The PESA procedure is applied to patients diagnosed with obstructive azoospermia due to any infection, vasectomy condition, or other cause. In cases where sperm cannot be obtained with the PESA method, the method of obtaining sperm from the testis is preferred. The application is a technique used only in cases of obstructive azoospermia. PESA application is performed on the same day as the egg collection date from the mother under local anaesthesia. The collected sperm are injected into the eggs taken from the mother after the microinjection method.
What is MESA IVF?
MESA IVF (Epididymal Sperm Aspiration Under Microscope) is the process of getting sperm from the epididymis via microsurgical techniques. It is usually applied for cases with sperm congestion. It is applied in case of normal or near-normal sperm production in the testis.
What is MESA in IVF treatment?
Another technique preferred commonly in IVF treatment is MESA. During the application, the sperm sample taken from the epididymis with fine needles is examined under a microscope. Since it is an invasive method, the healing process may take longer. However, the risk of blood accumulation called hematoma is also lower. The advantageous aspect of the MESA method is that even a small number of samples may be sufficient due to the high amount of sperm in the epididymis. IVF treatment combined with this technique is called MESA IVF.
What are the differences between MESA and TESA?
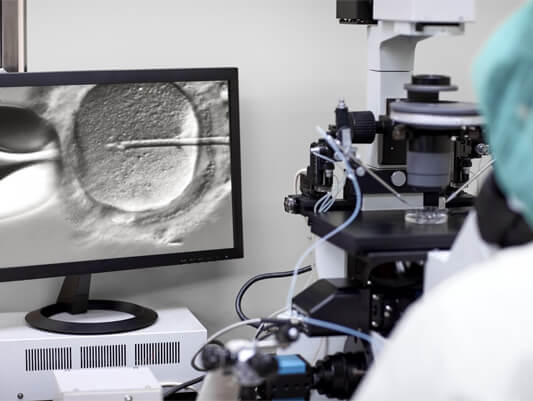
TESA is an application for obtaining sperm directly from the male testis without the use of urogenital routes. It is preferred for people who have had vasectomy surgery or whose surgery has been unsuccessful, patients who do not produce sperm, those who produce a small number of sperm due to some problems in the testicles, patients who do not have vas deferens or injuries in their ejaculatory ducts. It is a procedure performed under local anaesthesia. No incision on the skin is required.
In MESA application, sperm is obtained via microsurgical method by directly reaching the epididymis canal of the male. The number of sperm ducts to be cut from the relevant area is directly proportional to the desired sperm count and sperm motility. Sperm ducts are accessed through a small incision in the skin surrounding the ovaries, and samples are taken from this area to be examined under a microscope. It is usually done under general anaesthesia. It is an application where an incision on the skin is required.